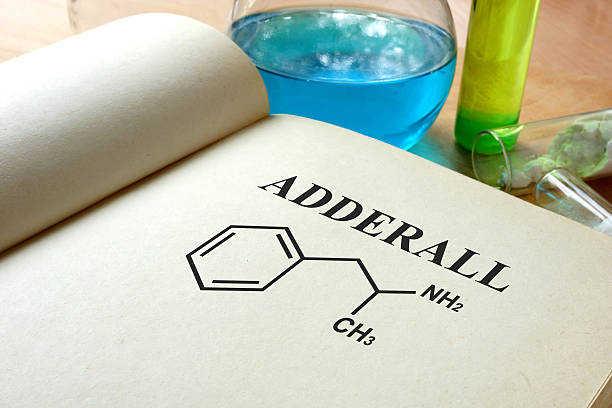
Adderall is a well-known stimulant medication prescribed mainly for ADHD (attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) and sometimes narcolepsy. It’s not a single chemical, but a mixture of amphetamine salts. Understanding how it was developed and how it’s manufactured requires looking at its history, its active ingredients, and the pharmaceutical regulation that shapes its production.
History & Development
- The roots of Adderall trace back to Obetrol, a weight-loss stimulant. Obetrol was later reformulated when issues arose with efficacy under U.S. regulations (the Kefauver-Harris Amendment) in the early 1970s. Specifically, Obetrol initially included two methamphetamine components; when reformulated, those were replaced with amphetamine and dextroamphetamine salts.
- Richwood Pharmaceuticals acquired the rights, reformulated the combination for ADHD and narcolepsy, and in 1994 started promoting the new version, which then became known as Adderall.
- Since that time, different formulations (instant release / immediate release (IR), and extended release (XR)) have been developed. The patent for certain versions has expired, allowing generic versions to enter the market.
Chemical Composition & Formulation
- Mixed amphetamine salts: Adderall doesn’t use a single amphetamine salt; rather, it’s composed of four salts:
- Amphetamine aspartate monohydrate
- Amphetamine sulfate
- Dextroamphetamine sulfate
- Dextroamphetamine saccharate
- The mixture of these salts helps achieve certain pharmacokinetic properties — for example, balancing how fast the drug acts, how long it lasts, and smoothing out peaks and troughs of effect. The IR formulation releases the active ingredients more rapidly; XR versions are designed for slower, prolonged release.
- In terms of inactive ingredients (binders, fillers, coatings, etc.), the exact compositions are proprietary, but like most oral tablets, Adderall’s tablet form uses excipients that support stability, manufacturability (powder flow, compressibility), and safe dissolution in the body. These might include things such as sugars or sugar substitutes, fillers (like lactose or similar), binders, disintegrants, coatings. (Note: specific excipient lists are part of pharmaceutical filing documents and might vary between manufacturers/generics.)
Sourcing of Active Ingredients & Regulatory Oversight
- The active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) underlying Adderall—the amphetamine salts—often rely on global supply chains. Raw chemical precursors might be sourced or synthesized in different countries (e.g., in Asia, or by specialized chemical suppliers), then shipped under regulatory oversight to manufacturing sites. While U.S. regulators oversee quality, inspections, and certifications, much of what happens abroad can be less immediately transparent.
- Because Adderall is a controlled substance, its manufacture is tightly regulated. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) sets production quotas (for amphetamine salts), tracks controlled substance production and distribution, enforces laws about handling, storage, and reporting. Additionally, the FDA reviews manufacturing practices (cGMP — current Good Manufacturing Practice), product labeling, stability, safety, and efficacy.
Tablet Manufacturing & Quality Control
While specific proprietary processes are generally not published in full detail, standard pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing steps apply, and what is known about Adderall aligns with typical practices:
- Blending / Mixing: The various amphetamine salts are accurately weighed, then blended with excipients to form a homogeneous powder blend.
- Granulation (if applicable): Depending on tablet design, wet or dry granulation may be used to improve flow and tablet consistency.
- Compression (tableting): The blend is pressed into tablets using tablet presses, under defined pressure settings. The shape, size, embossing or scoring (e.g., “dp” and “30” markings on some Adderall tablets) are part of the tooling. These markings help identify the tablet.
- Coating / finishing: Some tablets may be coated for ease of swallowing, protection from moisture, or to assist in controlling release (for extended release versions).
- Packaging: After tablets are made and tested, they are packaged — usually in bottles for IR Adderall (e.g. 100-count bottles) or blister packs if generics are different. Authentic packaging includes regulatory identifiers like the National Drug Code (NDC) and specific visual features (color, markings). Counterfeit versions often deviate from these norms.
- Quality control and testing: Throughout manufacturing, tests for purity of API, potency, tablet hardness, dissolution profile, stability over time (shelf life) are required. Particularly for extended release versions, measuring how the drug releases over time in vitro (in test conditions) is essential to ensure therapeutic equivalence.
Challenges & Manufacturing Constraints
- Supply chain issues for APIs: Shortages of active ingredients have been cited as a major factor in Adderall shortages. Because Adderall depends on amphetamine salts, any delays, raw material quality issues, or regulatory hold-ups abroad can ripple into domestic availability.
- Regulatory production limits: Because Adderall is a controlled substance, the DEA sets production quotas to limit misuse. Even when demand rises, the quotas restrict how much manufacturers can legally produce. This contributes to supply shortages especially during demand spikes.
- Counterfeit risk: With shortages and high demand, counterfeit or adulterated tablets have appeared. Examples include counterfeit 30 mg tablets that look similar but contain wrong active ingredients (e.g., tramadol and acetaminophen instead of amphetamine salts), wrong packaging, missing or wrong markings, or blister packaging vs. bottle packaging. Regulatory bodies issue safety alerts when such cases are discovered.
- Manufacturing enforcement: Changes in manufacturing plants, generics producers, and oversight matter a lot; companies making generics must produce formulations that are bioequivalent to the original, maintain consistent quality, pass inspections, etc. Any change (supplier, process, facility) often requires regulatory submissions, stability data, and equivalence testing.
Recent Developments
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals has announced that it will launch a generic version of Adderall tablets in May 2025, which is bioequivalent and therapeutically equivalent to the brand reference product. Such entries help increase supply and reduce costs.
- The ongoing shortage of Adderall in the U.S. since around October 2022 has been attributed to a combination of rising demand, difficulties obtaining active ingredients, regulatory constraints, and limited capacity.
Final Thoughts
The manufacturing of Adderall combines chemical synthesis of multiple amphetamine salts, pharmaceutical formulation using excipients, precise tableting, regulatory quality control, and very strict oversight because of its controlled-substance status. While we don’t have every proprietary detail (as companies guard many of their process secrets), public information reveals how the complex supply chain, regulatory limits, and tablet formulation all play essential roles. Problems in any of those areas—raw material supply, manufacturing capacity, regulatory compliance—can lead to shortages, counterfeiting, or changes in availability.